Understanding Chronic Inflammation – The Key to Preventing All Well-Being Diseases
Chronic inflammation-the big problem that goes unrecognized
Diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, even cancer; they all have one thing in common: chronic inflammation. We still do not know the exact cause of these disorders. But science suspects that chronic inflammation contributes to its occurrence. Chronic inflammation occurs when there is an accumulation of inflammatory cells that remain active when an infection is over or fought. We explain below.
We begin with our inflammatory response. Suppose you get a scrape on your leg, sprain your ankle or get a sore throat. In all cases, the area around the lesion swells. It gets filled with blood and feels warm; our inflammatory response. Our body sends white blood cells, fluid and proteins to the part that needs repair.
If your car is damaged, it will be repaired in the garage. When our body is damaged, our immune system helps with any possible infection. We refer to low inflammation levels as “suboptimal health.” You don’t feel optimal when your body puts energy into fighting an infection.

What is chronic inflammation?
Once the damage has been controlled and the risk of infection has passed, the white blood cells either die off or go back to doing what they did before; standing by in case of new injury. Chronic inflammation occurs when the infection does not go away. Or if the cells that helped fight it get “confused” and don’t spread. That causes an accumulation.
White blood cells that arrive at the site of injury are programmed to fight the inflammation. They turn off all damaged or infected cells, as they should. But once the infection is fought and the many white blood cells do not go away, they can start attacking healthy cells. The continued accumulation makes our immune system think there is still a problem. As a result, white blood cells become overzealous.
In such a scenario, you are dealing with the onset of chronic inflammation. If no remedy follows, the cells may go further out of control. They may then contribute to the development of certain types of cancer or the other diseases above.
Cytokines, a double-edged sword
You may be wondering what makes cells go haywire or why they attack healthy cells. This is due to cytokines.
Cytokines are small protein cells that deliver messages to various cells, including white blood cells. They are present in almost every biological process, but especially play a major role in our immune system. Cytokines can be divided into two camps: pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. For a properly functioning immune system, the right balance is essential. Consider that if there were no inflammatory response, we would not be able to fight an infection or virus.
Depending on the camp, cytokines deliver a message that tells white blood cells how to respond. Overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines creates a scenario in which white blood cells become overzealous. They then go on to attack healthy cells. The white blood cells get confused and keep thinking there is an infection to fight, when there is not.
If too many anti-inflammatory cytokines are present, our body cannot fight a virus or infection effectively. To be healthy, you need a balance of cytokines. This allows our immune system to know when action is required, as well as when it is no longer required.
The infographic below gives an overview of what can happen if you have too many pro-inflammatory cytokines, the balance is just right or if there is an accumulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
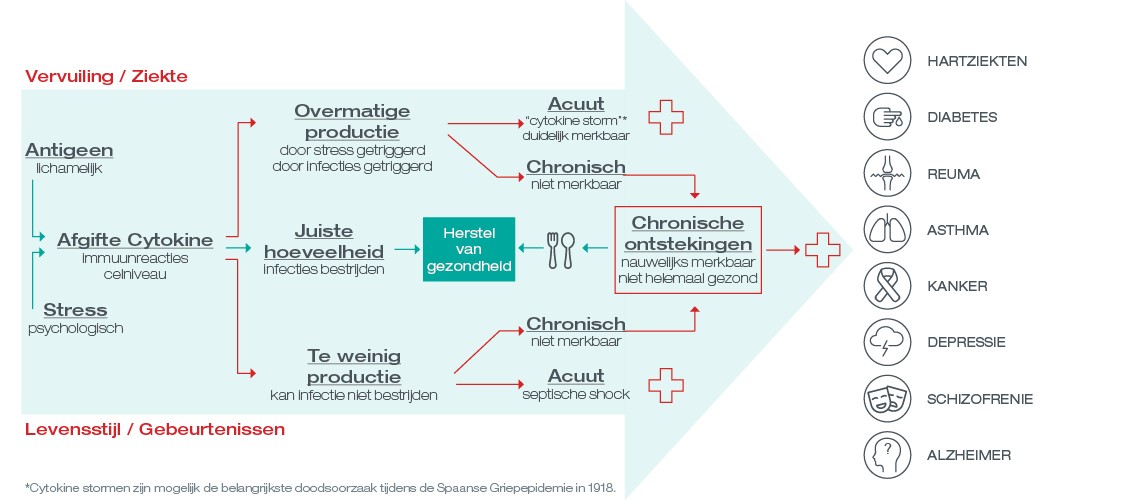
Chronic inflammation-hidden good news
Chronic inflammation seems quite frightening, especially since it may be the harbinger of serious illnesses. The World Health Organization marks such diseases as the greatest threat to human health. The link between chronic diseases and chronic inflammation is expected to strengthen further over the next 30 years, affecting millions of people.
But don’t panic!
So we know that chronic inflammation can cause diabetes, heart disease, arthritis and allergies. That means that fighting them might prevent these conditions from ever happening again. Once diagnosed with diabetes or heart disease? Then treatment can be incredibly difficult. However, chronic inflammation is much easier to manage.
Our diet has a huge impact on the production of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which tell our cells what to do. By improving our health with the right foods, we can provide balance. This allows us to effectively fight against the risk of chronic inflammation.
Foods to avoid
Try to avoid the following types of food for best results. However, limited consumption is also already beneficial. Each of these foods causes an inflammatory response:
– Deep-fried foods: For example, French fries, chicken and onion rings
– Refined carbohydrates: White bread, certain types of pasta and pastries
– Soft drinks: All drinks sweetened with sugar
– Red meat: Steaks fall into this category, but so do processed meats such as hot dogs and canned foods
– Margarine or lard
Foods you do need to eat
The following foods are beneficial to our health and help our bodies detoxify effectively. You can eat these foods as part of an anti-inflammatory diet. As a rule of thumb for a healthy balance, eat like our prehistoric ancestors. This is also known as the paleo diet. It’s about eating natural foods that cave people could hunt or gather. The food items all have anti-inflammatory effects:
– Tomatoes
– Nuts: For example, walnuts and almonds
– Oily fish: Species rich in omega 3, such as mackerel, tuna and salmon
– Fruit: Oranges, cherries, strawberries or blueberries
– Olive oil
– Hemp seed oil
Hemp as a nutrient, the new light
Final suggestion, cbd oil , is very important. Hemp has been recognized as a traditional medicine for inflammation for centuries. But despite its widespread use, modern medicine has not yet been able to verify its effects. It just so happens that many herbal remedies are used against inflammation. Therefore, they all have it in them to fight chronic inflammation.
Currently, modern medicine has yet to confirm the potency of hemp in treating inflammation. But that can change just like that. There are currently many research projects underway establishing how cannabinoids-chemical compounds from hemp-act on our endocannabinoid system (ECS). Our ECS is a regulatory system in our body. It is connected to parts in our brain, vital organs and our central nervous system. The interaction between the two may well be the key to hemp’s anti-inflammatory effects.
More and more research is being done on the medicinal effects of hemp. The possibility that it might help treat inflammation is therefore growing and growing. Hopefully, modern medicine will prove what traditional medicine has been trying to say for years.
