Cytokines Explained In 500 Words
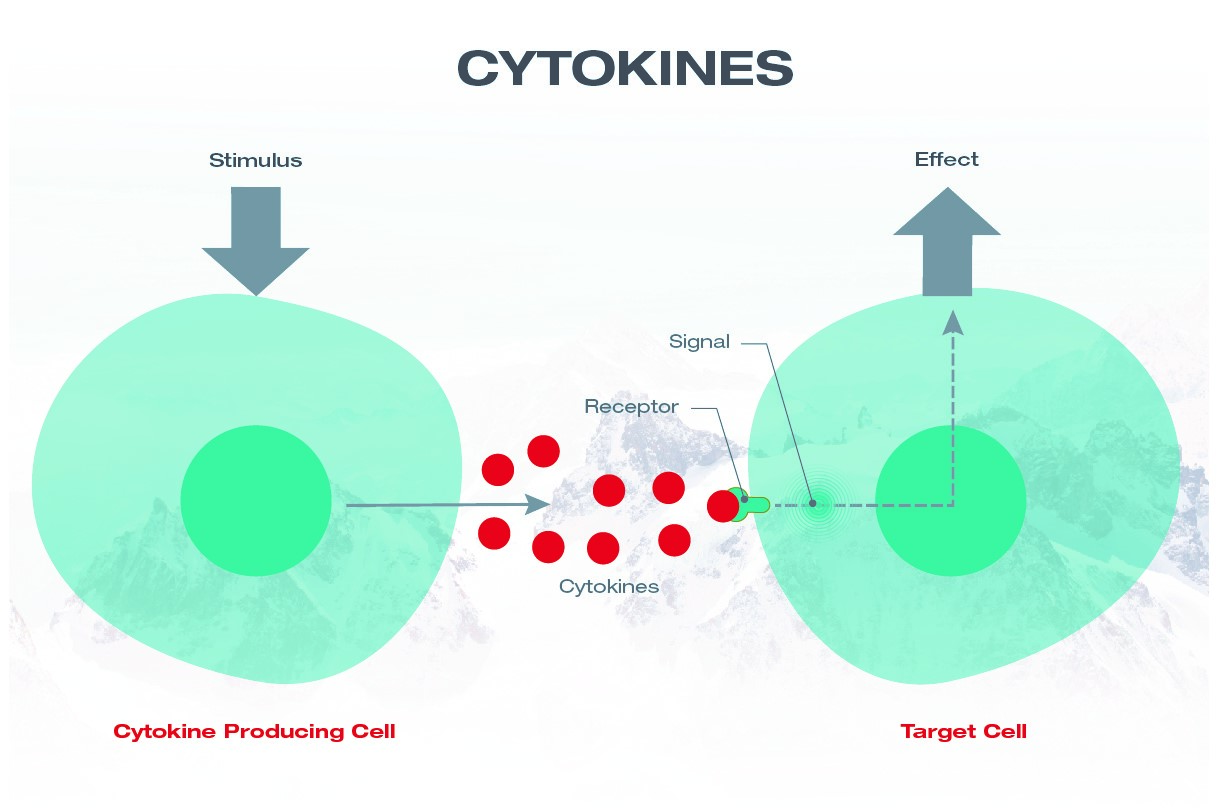
Cytokines are actually messengers. They carry a chemical message surrounded by protein molecules. The message depends on the type of cells with which the cytokines react or the type of cytokine. Cytokines occur in virtually every biological reaction. They prompt cells to replicate, develop and fight disease. But they can also cause cells to stop working.
Types of cytokines involved in immune responses
Cytokines are enormously diverse. You can therefore categorize them into several larger groups. This distinguishes between interferons, tumor necrosis factors and growth factors. These types all fall under the umbrella of “pro-inflammatory cytokines.” Pro-inflammatory cytokines cause a pro-inflammatory response in cells. However, anti-inflammatory cytokines (interleukins) do the opposite.
Cytokines-the frontier of modern medicine
By manipulating or stimulating cytokine production, a specific biological response can be induced. Therein lies the power of cytokines. Understanding how they work, how they are created and, most importantly, what biological response they unleash has enormous impact on treatment methods in modern medicine.
Damaging pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with the development of autoimmune diseases. These include rheumatism, arthritis, ischemic heart disease and gum disease. Moreover, research shows that these autoimmune diseases can further develop into tumors.
Of equal importance is the link between cancer and pro-inflammatory cytokines. For the treatment of certain types of cancer, therapeutic treatments that block or inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines could potentially be used. Cytokines are potentially hugely important in how we treat serious and fatal diseases.
Cytokine therapy-promising in the treatment of chronic diseases

Finding the balance of cytokines is crucial. Not only to defeat autoimmune diseases, but also for a healthy human body in general. That balance appears crucial when you consider that pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with cancer. Anti-inflammatory cytokines are thereby widely introduced as part of immunotherapy in cancer.
Synthesizing them in a lab can add more interleukin (anti-inflammatory) cytokines than our bodies produce. Interleukin 2 (IL-2), for example, stimulates antibody production. A cytokine similar to this, interferon-alpha (IFN-α), helps regenerate non-functioning immune cells.
Cytokine balance-the new focus on a healthy lifestyle
Fortunately, most of us ensure a healthy balance of cytokines through our diet. People on a gluten-free diet can especially benefit from a better balance in this regard. In fact, gluten may be linked to causing an inflammatory response. In addition, superfoods can stimulate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. This makes them a valuable component of our diet.
Thus, our food choices cause useful cytokines to be produced. But stress can activate our nervous system, blocking the vital functions of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Dealing well with stress therefore goes hand in hand with the natural, healthy production of cytokines and with good health in general.